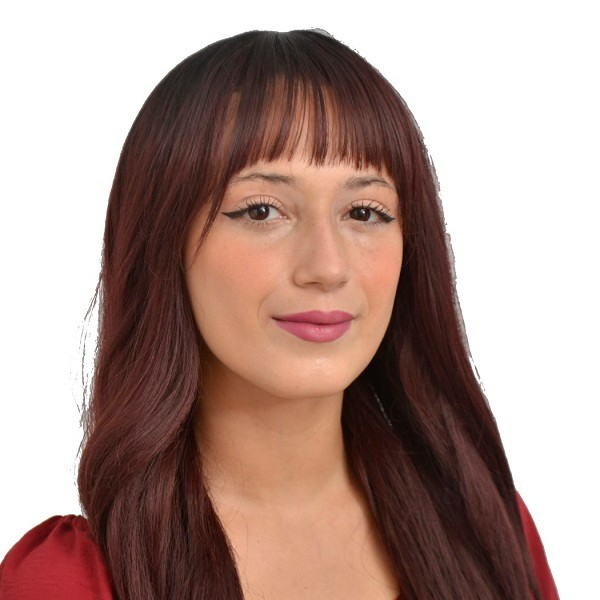
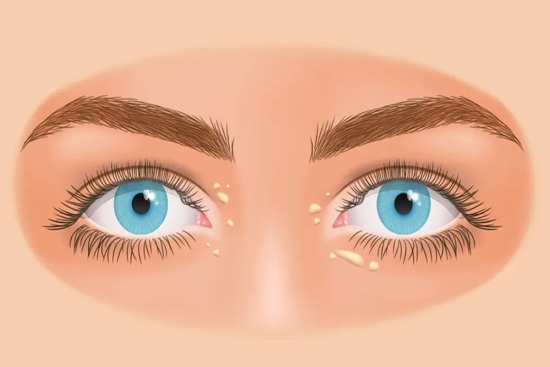
Xanthelasma palpebrae is a skin condition characterized by the accumulation of lipids (fats) on the eyelids, resulting in yellowish or whitish patches. Although not cancerous, these lesions result from excess cholesterol in the blood and may be associated with other health problems.
In Turkey, medical and surgical treatments are available to remove these plaques and improve the appearance of the eyelids.
- People with cholesterol deposits under the skin around the eyes, causing yellow or whitish spots.
- Scars.
- Bleeding.
- Infections.
- Loss of skin pigmentation.
- It all depends on the type of treatment chosen and the severity of the condition.
Best Clinics with Verified Reviews

- Multispecialized hospital
- 7 operating rooms
- Capacity é of 170 beds

- Multispecialized hospital
- Hospital founded in 2007
- Very good reputation in ENT department
Xanthelasma: What is it?
Xanthelasma is a skin condition characterized by soft, yellowish or beige-colored growths that develop on the eyelids and around the eyes.
They consist of fatty deposits that accumulate under the skin, forming a raised or flat, irregular patch.
Although harmless in most cases, xanthelasma can sometimes be associated with lipid metabolism disorders such as hypercholesterolemia and, more rarely, with cardiovascular pathologies.
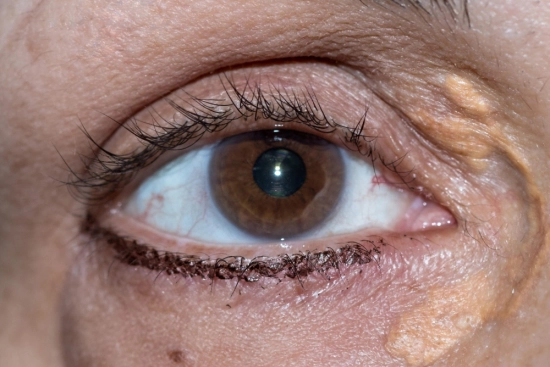
Causes of Xanthelasma palpebrarum
The appearance of yellow patches of xanthelasma on the eyelids is generally associated with a lipid imbalance in the body. Risk factors include:
- Dyslipidemia: An excess of cholesterol or triglycerides in the blood.
- Hypothyroidism: Abnormal thyroid function.
- Liver diseases: such as cirrhosis of the liver or primary biliary cirrhosis, that affect lipid metabolism.
- Pancreatitis: Rarely, inflammation of the pancreas may be associated with the appearance of xanthelasma.
Xanthelasma may be an important marker of underlying systemic disease. In fact, in about 50% of cases, xanthelasma is associated with hyperlipidemia, an excess of fats (lipids) in the blood. This association is particularly pronounced in men. The early onset of xanthelasma, before the age of 40, strongly suggests familial hypercholesterolemia.
Excess lipids, particularly LDL cholesterol (considered "bad" cholesterol),can accumulate in the artery walls and promote the development of atherosclerosis. In the long term, this condition increases the risk of serious cardiovascular disease such as heart attack and stroke.
Xanthelasmas do not cause itching or eyelid pain, nor do they cause any ocular symptoms.
Diagnosis of xanthelasma in Turkey
In Turkey, xanthelasma is diagnosed by clinical examination. If you notice the appearance of yellowish, often soft and slightly raised spots around the eyes, especially in the inner corner (medial canthus),it's advisable to consult an ophthalmologist. These characteristic lesions are often a sign of xanthelasma.
The ophthalmologist will make a visual diagnosis and may order blood tests, including a lipid profile. The latter allows the assessment of total cholesterol, HDL (good cholesterol),LDL (bad cholesterol),and triglyceride levels. These tests are essential to determine if xanthelasma is associated with a lipid imbalance and to determine appropriate treatment.
Xanthelasma Treatments in Turkey
Surgeons perform xanthelasma removal, at our partner clinics in Turkey, through several treatments. The main options are as follows:
Surgical removal
Xanthelasma treatment involves the surgical removal of lipid deposits. This excision technique is usually used for very hard and deep lesions, i.e. larger than 3 mm.
This procedure is usually performed under local anesthesia and on an outpatient basis (without hospitalization). The oculoplastic surgeon gently removes the skin patches and uses sutures to close the area.
Surgical removal greatly reduces the risk of recurrence months or years later. If surgical removal is preferred, an upper blepharoplasty with simultaneous palpebral reshaping is usually suggested. In this case, there is no need to be afraid of visible scars. On the contrary, the result is always natural and harmonious.
CO2 ablative laser treatment
If you are looking for a non-invasive method, the CO2 laser is highly recommended. The CO2 laser treatment acts on the surface of the skin thanks to a light beam that pulverizes the xanthelasma without damaging the surrounding tissue. Anesthesia is not required, but an anesthetic cream must be applied before the procedure. The lesion heals quickly and without scarring.
Whatever the size, location, or cause of xanthelasma, it's important to consult a doctor specializing in aesthetic medicine or dermatological care, who can advise you on the best course of action.
In conclusion, xanthelasma is an unsightly but treatable skin condition. If you are concerned about the appearance of patches around your eyelids, consult your physician to discuss the most appropriate treatment options for you.
Share this page
Xanthelasma can potentially reappear even after treatment, especially if the underlying cause, such as high cholesterol, is not adequately addressed. Lifestyle modifications, including a healthy diet and exercise, can help prevent recurrence.
The appearance of xanthelasma is strongly associated with a diet rich in fat, so after its removal, it may reappear if the patient does not follow a diet low in triglycerides and cholesterol.
No, xanthelasma palpebrarum can't disappear on its own, on the contrary, it can grow in size, which can be embarrassing for anyone, especially when it comes to physical appearance. So it's best to consult a dermatologist for treatment.
Yes, the appearance of xanthelasma should never be overlooked as it is often associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. So it's so important to visit a doctor to evaluate your lipid panel and undergo the appropriate treatment.