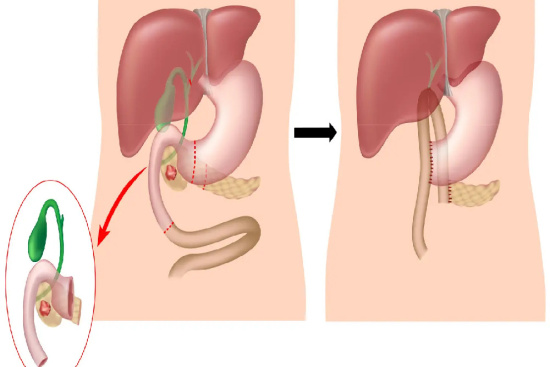
Has your doctor recommended Whipple surgery (pancreaticoduodenectomy) to address a serious condition affecting your pancreas, bile ducts, or nearby organs?
If you're considering undergoing this complex procedure abroad, Turkey has become a top destination for international patients seeking high-quality care. With internationally accredited hospitals, experienced surgical teams, and significantly lower treatment costs, Turkey offers a safe and effective alternative.
Get in touch with our medical advisors today for a free consultation and personalized treatment plan tailored to your needs in Turkey.