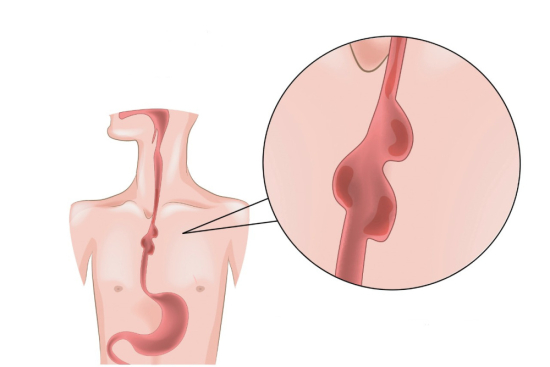
Living with an esophageal diverticulum can cause significant discomfort and lead to serious complications. When surgery becomes necessary, Turkey offers a reliable and attractive treatment option.
With advanced medical infrastructure, highly skilled digestive surgeons, and more affordable treatment costs, Turkey has become a preferred destination for esophageal diverticulum surgery, attracting patients from around the world seeking high-quality care and optimal outcomes.
Cost of an esophageal diverticulum surgery in Turkey
The cost of esophageal diverticulum surgery in Turkey varies depending on the type and complexity of the procedure.
With Turquie Santé, you can benefit from surgery performed by highly skilled specialists in partner clinics equipped with state-of-the-art medical technology.
From your preoperative consultation to postoperative follow-up, we provide support and guidance every step of the way to ensure a safe and comfortable experience.
Contact us today to plan your medical stay in Turkey with confidence and receive personalized guidance for your treatment.