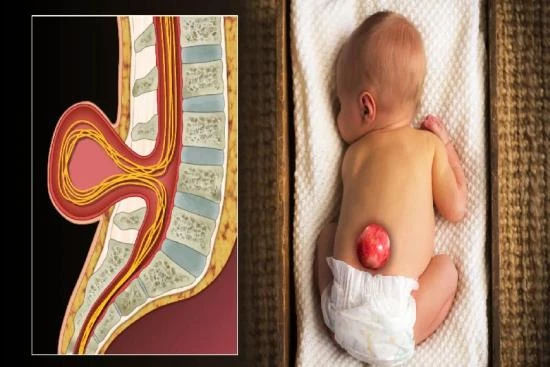
Spina bifida is a congenital malformation characterized by a defect in the closure of the spinal column. This neurological disorder, which varies in severity, often requires specialized medical care throughout life.
In fact, depending on the severity and location of the anomaly, spina bifida can lead to a variety of health problems ranging from mild sensory impairment to more severe paralysis.
Risks and Side Effects
- Incision healing.
- Infection.
- Hydrocephalus.
- Chiari malformation.