Years of indoor tanning and excessive exposure to ultraviolet rays can cause a variety of problems for your skin. These UV rays damage the DNA of skin cells, promoting the appearance of malignant tumors such as melanomas, which are particularly aggressive, and carcinomas.
With millions of cases reported each year, skin cancer is cited as one of the most serious potential problems.
In Turkey, excision is the treatment of choice for the majority of skin cancers.
- Persons with BCC
- Persons with melanoma
- Persons with advanced or metastatic skin cancer
- Ecchymosis
- Skin peeling
- Itching
- Complementary and integrative medicine
- Herbal Therapies
- Nutritional supplements
- >90%
Best Clinics with Verified Reviews

- Multispecialized hospital
- 7 operating rooms
- Capacity é of 170 beds

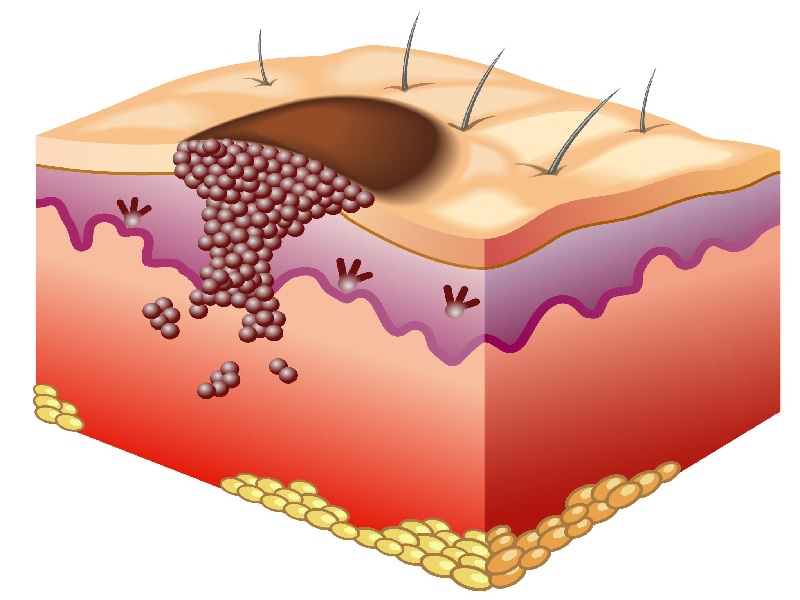
Skin cancer: What is it?
Skin cancer is a disease characterized by the abnormal, uncontrolled proliferation of skin cells. These mutations are mainly caused by UV radiation, but also by intrinsic (genetic) and extrinsic (environmental) factors.
Keratoses, basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma are the most common forms of skin cancer. Early diagnosis is essential for effective treatment.
With your health in mind, our expert dermatologists offer a complete skin assessment. Don't wait to make an appointment and benefit from an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.

Types of skin cancer
The different types of skin cancer include:
- Actinic keratoses (AK): These scaly, rough skin lesions are considered precancerous. They usually appear on areas of the body most exposed to the sun (face, neck, hands, forearms) in fair-skinned people over the age of 40. If left untreated, actinic keratoses can develop into squamous cell skin cancer.
- Basal cell carcinoma (BCC): This is the most common type of non-melanoma skin cancer. It often appears as a small, pearly, translucent or pink lesion. BCC develops slowly and tends to localize on the head and neck. Although rarely fatal, it can cause significant damage to surrounding tissue if not treated in time.
- Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): This type of skin cancer develops from cells in the outer layer of the skin. It appears as a red, scaly, or crusty lesion. CEC can occur anywhere on the body, but is more common in sun-exposed areas. It can develop more rapidly and be more invasive than basal cell carcinoma.
- Melanoma: This is the most dangerous form of skin cancer. It develops in melanocytes, the cells that produce melanin (the pigment responsible for skin color). Melanomas can occur on healthy skin or from an existing mole. They are often asymmetrical, unevenly colored, with irregular edges, and larger than 6 mm in diameter.
Skin cancer treatment options in Turkey
Skin cancer is a complex disease that requires individualized treatment. In Turkey, patients benefit from the latest medical expertise and a wide range of treatments to eradicate cancer cells while preserving as much healthy tissue as possible.
Surgery: the basic treatment
Surgery remains the most common treatment for skin cancer. It involves the removal of the tumor and a margin of healthy skin to minimize the risk of recurrence.
There are several surgical techniques, including:
- Simple excision.
- Mohs surgery (especially precise for complex tumors).
- Laser surgery.
The choice of surgical technique depends on several factors, including the type of cancer, its size and location, and the patient's general condition.
Alternative treatments
In some cases, other treatments may be considered:
- Cryotherapy: Destruction of cancer cells using cold.
- Anticancer creams: Local application of medicines to eliminate superficial lesions.
- Radiation therapy: Use of radiation to destroy cancer cells.
- Photodynamic therapy (PDT): Combination of photosensitizing drugs and light to destroy cancer cells.
The choice of the most appropriate treatment is made in close collaboration between the patient and the medical team, taking into account the individual characteristics of each case.
Process of skin cancer surgery
Surgery to remove a skin tumor involves several essential steps:
Diagnostic evaluation
The treatment of a skin tumor begins with a thorough diagnosis. The skin lesion in question will be examined by a dermatologist or oncologist, who may also perform a biopsy to confirm the presence of cancer cells.
Planning a treatment strategy
Once the diagnosis has been made, the surgeon will draw up a customized treatment plan. He takes into account the size, location and type of tumor to select the most appropriate surgical technique.
Tumor removal surgery
The procedure is usually performed under local anesthetic, which allows the patient to remain awake and unaffected by pain.
To ensure that all cancer cells are removed, the surgeon removes the cancerous tissue and a margin of healthy skin around it. To ensure that the cancer has been completely eliminated, further tests are then carried out on the excised tissue.
To promote healing and reduce scarring, the wound is then cosmetically closed using sutures, staples or other suitable techniques.
Side effects of skin cancer removal surgery
Although skin cancer removal surgery is usually painless and safe, some side effects may occur:
- Risk of infection at the surgical site.
- Scarring of the skin.
- Bleeding during or after surgery: In most cases, this can be controlled with additional pressure or stitches.
- Numbness or nerve damage (change in skin sensitivity).
- Fatigue.
- Edema.
Healing process
Post-operative skin tumor removal care is essential for proper healing and a speedy recovery.
You may need a family member or friend to help you with daily tasks until you feel better. It may take some time before you can resume your normal activities.
Be sure to take your prescribed medications as directed to prevent pain, infection, and/or constipation. Call your care team with any new or worsening symptoms.
There are ways to treat constipation after surgery. You can change your diet, drink more fluids, and take over-the-counter medications. Talk to your healthcare team before taking laxatives.
Success rate of skin cancer treatment in Turkey
Cutaneous basal cell carcinoma does not usually invade other organs of the body. Resulting in low rates (no more than 5%) of BCC spreading to other parts of the body.. However, for both BCC and ECC, considerable skin damage can sometimes occur if the tumor is left untreated.
In our partner clinics, 90% of non-melanoma skin cancer cases have been successfully treated. Subsequently, the success rate of this treatment in our partner hospitals and medical centers in Turkey is considered very high.
In addition, Turquie Santé strives to offer you the best melanoma and carcinoma treatment costs with the highest quality of service in Turkey. Costs include all cancer-related care, from diagnosis to treatment, follow-up and use of healthcare resources.
Share this page
- Protect your skin from the sun by wearing hats and applying sunscreens with a sun protection factor of at least 30;
- Avoid tanning salons;
- Eat enough foods rich in vitamin D;
- Check for any changes in your skin (moles, a wart, a skin lesion that would not heal).
The signs that show you may have skin cancer are:
- Encrusted lesion which bleeds, does not heal or recurs after healing;
- Flat, pale or yellow area resembling a scar;
- Red or pink, scaly patches with irregular, raised edges;
- Small smooth and shiny patches, white, pink or red;
- A mass with small veins on the surface;
- Irritated and itchy areas;
- A wart-like skin growth.
- Exposure to ultraviolet rays (tanning, PUVA treatment);
- Pallor (weak secretion of melanin);
- Exposure to ionizing radiation (α, β, X or γ);
- Contact with Arsenic;
- Working with certain products (bedded clay, tar, charcoal, creosote, etc.)
- Xeroderma pigmentosum disease: a disease that causes sensitivity to extreme rays to ultraviolet rays;
- Gorlin Syndrome (Basal Cell Nævomatosis): a very rare genetic disease characterized by a predisposition to develop several cancers.
- Immunosuppressive diseases.
The main treatment for skin cancer in our partner clinics in Turkey is surgery. There is also targeted therapy and immunotherapy.