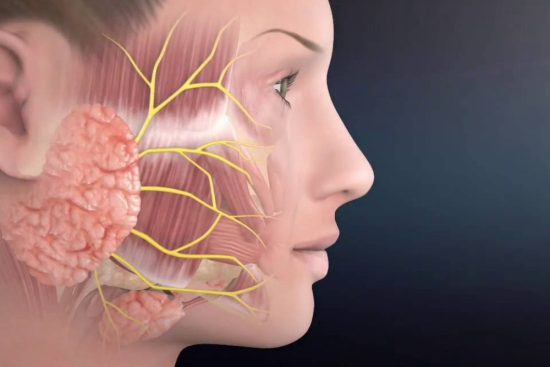
Parotidectomy is a common procedure performed by otolaryngologists in Turkey to treat various conditions of the parotid gland, such as tumors, cysts, or infections. The surgery is typically done using minimally invasive techniques to minimize scarring and reduce the risk of complications.