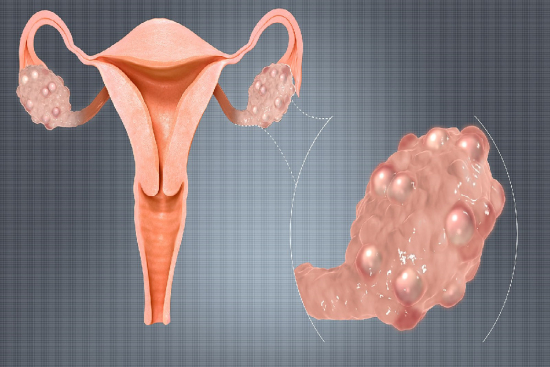
Have you ever heard of ovarian cysts? Don't panic! These small, fluid-filled sacs are very common in women and are usually benign.
Treatment of ovarian cysts is mainly based on regular monitoring, but surgery may be needed if there are complications or persistent symptoms.
- Women with large or rapidly growing ovarian cysts and troublesome symptoms.
- Pelvic pain.
- Bloating.
- Light bleeding.
- Infections.
- Between 30 minutes and 1 hour.
Cost of ovarian cyst removal surgery in Turkey
The cost of ovarian cyst removal surgery in Turkey generally varies between 2,500 and 3,750 Dollars.
Choose Turquie Santé and benefit from high quality medical care at competitive prices.
Our partners, ultra-modern clinics equipped with the latest technology, offer you personalized care by experienced surgeons. Turquie Santé takes care of everything: flights, accommodation, surgery and post-operative care. Request your free quote now!
Best Clinics with Verified Reviews

- Multispecialized hospital
- 7 operating rooms
- Capacity é of 170 beds
Ovarian cysts: What are they?
The ovaries, located in the female pelvis, play an important role in reproduction by producing eggs and the female sex hormones estrogen and progesterone. However, a cyst - a pocket containing a fluid or semisolid substance - can develop within an ovary.
Although they can cause symptoms, the majority of ovarian cysts are benign and do not require specific treatment.
The types of ovarian cysts are varied, including hormone-related functional cysts and organic cysts of various origins. Although the majority are painless and require no treatment, their presence may require regular medical surveillance.
Types of ovarian cysts
The pathology of ovarian cysts falls into two main categories:
- Functional cysts: Associated with the menstrual cycle, these are the most common and often disappear spontaneously. They include follicular cysts, which form when a follicle fails to release an egg, and corpus luteum cysts, which appear after ovulation.
- Organic cysts: Independent of the menstrual cycle, these have more varied origins. They include serous cysts (filled with a clear fluid),dermoid cysts (containing various tissues such as hair or teeth),endometriotic cysts (associated with endometriosis),mucoid cysts (filled with a viscous fluid),and, more rarely, cancerous cysts.
Factors that may favor the development of ovarian cysts
The formation of ovarian cysts is a common phenomenon, often associated with menstrual cycles. However, certain factors may favor their appearance:
- Menstrual irregularities.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
- Endometriosis.
- Family history.
- Certain hormone treatments (such as those used for breast cancer) and childbearing age.
Although these ovarian cysts are usually benign, they may require medical attention.
Symptoms of ovarian cysts
The symptoms of ovarian cysts vary depending on their size and location. Small cysts are often silent. Larger cysts, on the other hand, may cause:
- Pelvic pain.
- A feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen.
- Abdominal swelling.
- Urinary problems or irregular periods.
- Dyspareunia (pain during sexual intercourse).
The persistence of these symptoms, combined with other signs such as excessive hair growth or difficulty losing weight, may indicate polycystic ovary syndrome.
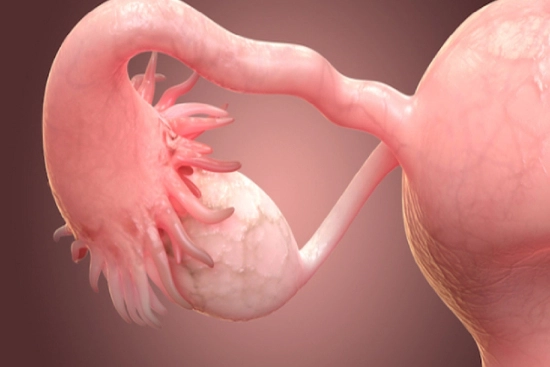
Complications related to ovarian cysts
Ovarian cysts can pose a risk of complications. The most common include:
- Rupture: The cyst may rupture, causing sudden, severe abdominal pain, sometimes accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
- Torsion: The cyst may twist on itself, cutting off the blood supply to the ovary. This is a medical emergency requiring prompt surgical intervention to prevent ovarian necrosis.
Diagnosis of ovarian cysts
Diagnosing an ovarian cyst requires a combined approach. After a thorough history and examination, a clinical examination is performed.
Pelvic ultrasound, the gold standard, allows accurate visualization of the cyst.
Additional tests, such as blood work or imaging, may be needed to refine the diagnosis and rule out other conditions.
Treatment of ovarian cysts in Turkey
The treatment of an ovarian cyst in Turkey is individualized and depends on a number of factors, such as the patient's age, the size of the cyst, its type (benign or malignant),and the presence or absence of symptoms.
In many cases, simple medical surveillance is sufficient, as functional cysts tend to resolve spontaneously. Suppose symptoms are bothersome or the cyst persists. In that case, various treatment options may be suggested: hormonal medical treatment to regulate the menstrual cycle and prevent the formation of new cysts, or surgery to remove the cyst.
If cancer is suspected, specialized treatment by a gynecologic oncologist is essential.
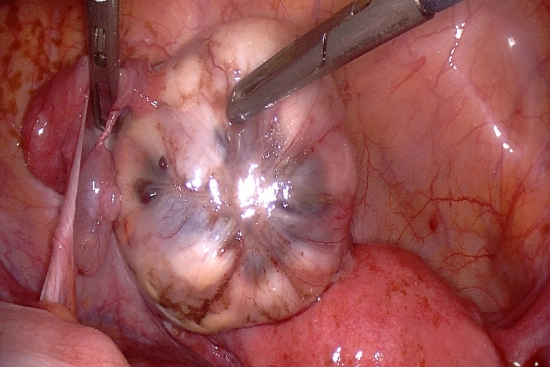
Removal of ovarian cysts
Surgery to remove an ovarian cyst depends on the size of the cyst, its location, and the patient's overall health. Most surgeries are performed using laparoscopy, a minimally invasive technique that requires small incisions in the abdomen.
- Laparoscopy: The surgeon inserts an instrument with a camera (the laparoscope) and surgical tools through these small incisions. The surgeon views the inside of the abdomen on a screen and proceeds to remove the cyst.
- Laparotomy: In some cases, a larger incision may be needed, for example, if the cyst is very large or if there are significant adhesions.
Recovery from laparoscopy is generally quicker than from laparotomy, with moderate postoperative pain relieved by analgesics.
It is advisable to rest for the first few days, limit physical exertion for a few weeks, and gradually return to a normal routine.
Share this page