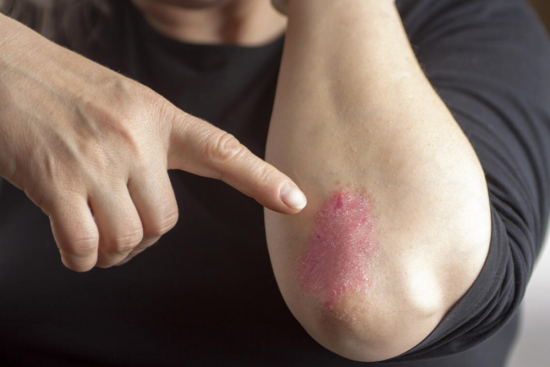
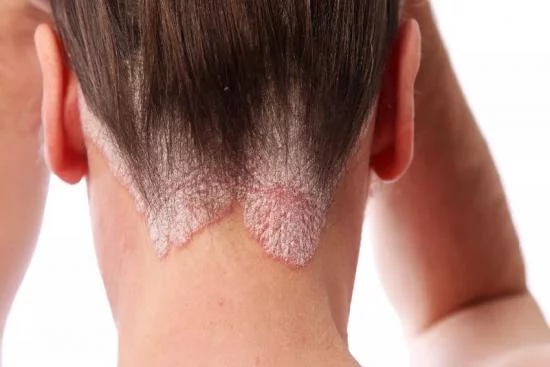
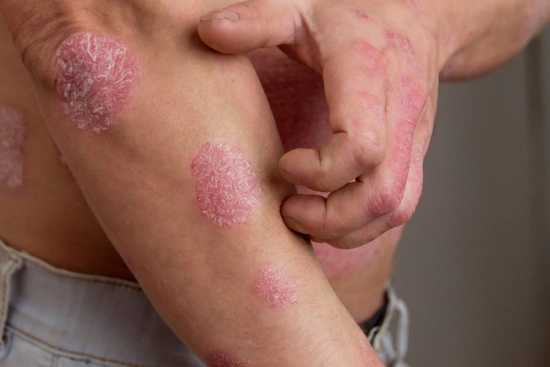
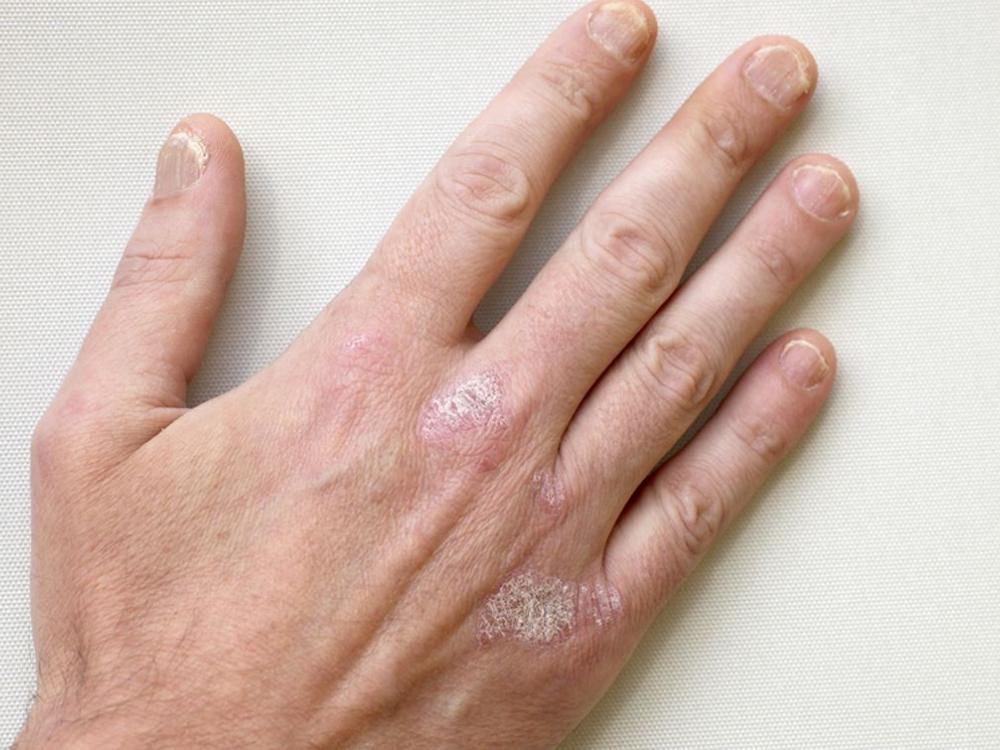
Red, scaly patches on the knees, elbows, or scalp can be more than just a skin issue. They can affect your comfort, confidence, and daily life. Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that requires proper management to relieve symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
With experienced dermatologists in Turkey, effective treatments are available to soothe your skin, reduce symptoms, and improve your quality of life.
Psoriasis treatment costs in Turkey with Turquie Santé
Receiving psoriasis treatment in Turkey combines high-quality care with affordable prices. The cost of treatment varies depending on the severity of the condition and the type of therapy recommended, such as topical treatments, phototherapy, or advanced biologic therapy. On average, prices range from $300 to $1,500 per treatment plan.
With Turquie Santé, you benefit from full support throughout your treatment journey. From consultation and evaluation to follow-up care, our team ensures that your care is professional, safe, and tailored to your needs.
Contact Turquie Santé today to schedule your consultation and receive expert psoriasis care in Turkey at competitive rates.