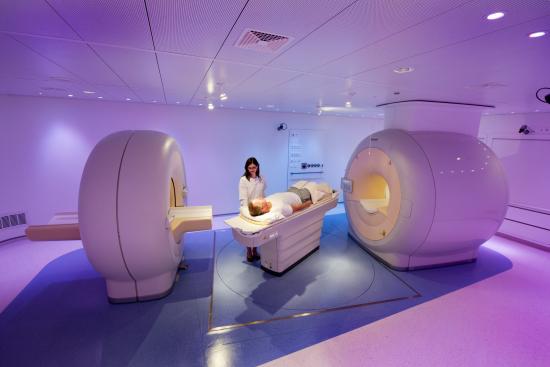
Are you facing medical uncertainty? Waiting for clear, fast, and reliable answers? The PET scan (or PET-CT) is today one of the most advanced imaging tests for the early detection of cellular abnormalities in the body.
This high-precision examination relies on cutting-edge technology capable of visualizing the metabolic activity of cells, well before any abnormality becomes visible on a conventional CT scan or MRI.
How much does a PET-Scan cost in Turkey?
In Turkey, the cost of a PET-Scan ranges between €350 and €700.
This price generally includes:
- A pre-exam consultation with a specialist
- The injection of the radiopharmaceutical tracer
- The PET-CT scan itself
- Image interpretation by a nuclear medicine physician
- A bilingual medical report (FR/EN)
Need a precise quote or a fast appointment? Our teams in Turkey support you from A to Z : from initial contact to delivery of results, with full transparency.
Contact us today to receive a personalized estimate or schedule your scan as soon as possible.