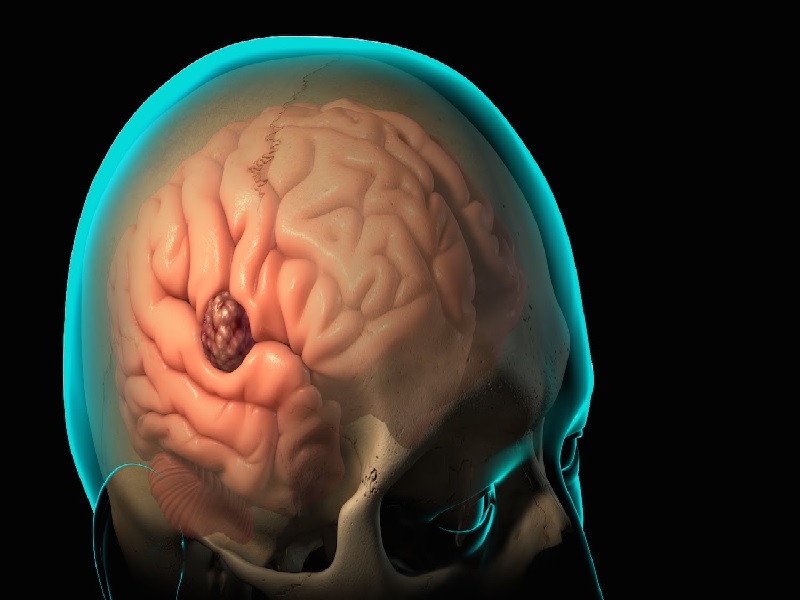
A meningioma is a tumor that develops from the meninges' cells, the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord. Although generally benign (non-cancerous),this tumor can sometimes become problematic due to its growth, which can put pressure on the brain.
In most cases, meningiomas are noncancerous and grow slowly. However, some can become aggressive and require urgent treatment to avoid more serious risks. If you have been diagnosed or are showing symptoms, prompt treatment at specialized clinics in Turkey can be crucial to prevent complications.
Best Clinics with Verified Reviews

- Multispecialized hospital
- 7 operating rooms
- Capacity é of 170 beds

Symptoms of meningioma: What to look for?
Initially, a meningioma may be completely asymptomatic, leaving the patient unaware of the tumor's presence. However, as it grows, the pressure it exerts on the brain can cause symptoms that vary depending on several factors, including:
- Location: This determines the brain area affected by the compression.
- Size: The larger the tumor, the greater the compression on the brain tissue.
Signs and symptoms of a meningioma usually develop gradually, increasing in intensity as the mass grows. The most common symptoms include:
- Vision changes: double vision or blurred vision.
- Headache: increasing pain over time.
- Hearing loss or ringing in the ears.
- Memory loss.
- Loss of sense of smell.
- Muscle weakness in arms or legs
- Hair loss.
- Involuntary weight loss.
Although most meningioma symptoms develop slowly, some cases may require emergency medical attention. Suppose you are experiencing signs of this brain tumor. In that case, it's important to consult a specialist, especially in Turkey, where advanced treatments are available to manage and treat this condition.
Act quickly to protect your health: learn more about specialized meningioma treatments in Turkey.

Causes of meningeal tumors
Meningiomas, which account for about 30% of all brain tumors, primarily affect women, adults, and the elderly. The risk of developing this tumor increases with age and is even higher in individuals with a family history of neurofibromatosis, a genetic disorder that favors the formation of benign tumors in the meninges and nerves.
Exposure to ionizing radiation is also a well-established risk factor for the development of meningiomas. Patients who have received cranial irradiation, especially during childhood, have an increased risk of developing this tumor.
Pay close attention to your medical history and consult a specialist if you have any risk factors.

Early diagnosis of Meningioma: Key tests
Meningiomas can often go undetected, especially if they are asymptomatic. In some cases, they are discovered incidentally during tests performed for other reasons, such as after a head injury.
However, the symptoms of a meningioma can sometimes be confused, at least initially, with normal signs of aging, which can delay diagnosis and access to appropriate treatment.
The diagnosis of meningioma involves several key steps, including:
- Clinical examination: A healthcare professional will evaluate the patient's symptoms.
- Medical imaging: Advanced techniques such as MRI, CT, or PET scans may be used to locate and characterize the tumor.
- Brain biopsy: A sample of the tumor may be removed and analyzed to confirm its type.
- Other tests: Additional tests such as an eye exam, electroencephalogram (EEG),or neuropsychological evaluation may be performed, especially if surgery is being considered.
Early detection and thorough medical evaluation are essential to ensure prompt and effective treatment of meningiomas.
Consult one of our partner specialists in Turkey today for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options.

Meningioma treatment options in Turkey
Treatment of meningioma in Turkey is mainly based on a surgical approach. However, in some cases, especially for small tumors with no visible symptoms, watchful waiting may be recommended by specialists such as oncologists or neurosurgeons.
Surgery: the main solution
Surgery is the most effective way to remove a meningioma, especially if it is large, misplaced, or causing neurological symptoms. The procedure varies depending on the location of the tumor, but generally, a craniotomy (opening of the skull) is required to gain access to the inside of the skull.
In Turkey, recent technological advances allow surgeons to precisely locate the tumor, define its boundaries, and preserve vital areas of the brain, making the surgery safer and less invasive.
Our partner hospitals in Turkey use cutting edge technologies such as neuronavigation, neuromonitoring, endoscopy, ultrasound scalpels and microdoppler. These tools allow for more precise surgery and faster recovery, while minimizing the risk of damage to functional brain tissue.
When is surgery not necessary?
In many cases, an MRI is sufficient to confirm the presence of a meningioma. If your neurosurgeon recommends surveillance rather than surgery, it usually means that the tumor is benign, stable, and not an immediate threat. Surgery is most often suggested when a meningioma is increasing in size or is located in an area where it is causing neurological symptoms.
Complex cases
If the meningioma is located in critical areas of the brain, such as those responsible for motor skills or speech, or if it is in contact with important veins (such as the superior longitudinal sinus),complete removal of the tumor may be complex. In these cases, the neurosurgeon may not be able to remove the entire tumor, which may require close monitoring or targeted radiation therapy.
For recurrent or incomplete meningiomas, radiation therapy may be used to shrink residual tumors. Chemotherapy is rarely used to treat this tumor.

Probability of cure
The likelihood that a meningioma will be cured depends on several key factors, including the type of tumor, stage of progression, available treatment options, and the patient's age and overall health.
For benign brain tumors such as meningiomas, which tend to progress slowly, the cure rate is very high. Thanks to advanced treatments and early detection, many patients make a full recovery after surgery.
In contrast, malignant tumors, which develop rapidly, often have a poorer prognosis. However, current research and therapeutic advances promise to improve the chances of cure for these more complex cases.
Although meningiomas are often benign, there is a risk of malignant transformation in some cases. When this occurs, the tumor may become more aggressive, with a higher degree of anaplasia. Malignant transformation remains a major uncertainty, but is relatively rare, especially with appropriate medical follow-up.
Share this page