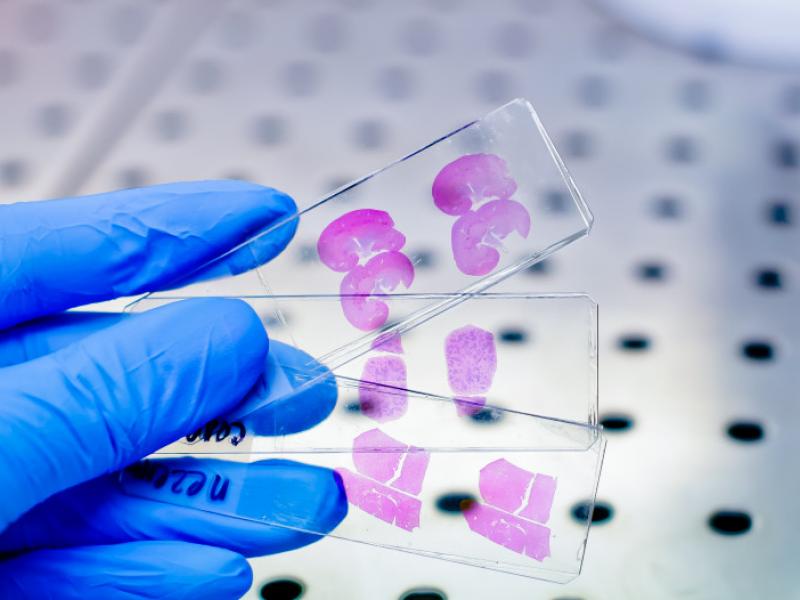
A liver biopsy is a medical procedure in which a fragment of liver tissue is removed with a special needle and inspected under a microscope to identify and characterize various liver diseases.
Liver biopsy in Turkey is well performed in our partner clinics! It can therefore be used as a diagnostic tool when liver disease is suspected and cannot be investigated by other techniques, or as a tool to determine the severity of the disease when it has already been established by other means.
This treatment is reserved for people in whom there is:
- An increase in transaminases (enzymes indicating liver damage)
- A positive viral DNA test (PCR)
- Hematoma
- Hemorrhage in the peritoneum
- Infection
- Fibrotes
- Fibroscan
- Five to ten minutes
How much does the treatment cost in Turkey?
Turquie Santé is at your disposal to provide you with the best clinics in Istanbul Turkey to perform a liver biopsy in the right conditions and at the best cost. Experienced doctors will take care of performing your procedure in the best hospitals or clinics in Turkey, Izmir, Antalya, and Ankara.
Best Clinics with Verified Reviews

- Multispecialized hospital
- 7 operating rooms
- Capacity é of 170 beds
Liver biopsy procedure in Turkey
A liver biopsy procedure in Istanbul, Turkey can be used to determine the severity of the liver disease. This information helps in making treatment decisions. However, the most common type of liver biopsy is (percutaneous liver biopsy).
A tiny bit of tissue is extracted from the liver during this sort of biopsy after a thin needle is introduced through the abdomen. Two other types of liver biopsies use a needle to remove liver tissue; one uses a vein in the neck (intravenous),and the other uses a small incision in the abdomen (laparoscopic).
Indications of hepatic biopsy
A liver biopsy may be done for the following reasons:
- Diagnose a liver issue that cannot be identified otherwise.
- Obtain a tissue sample for a malformation identified during an imaging examination.
- Assess the severity of the liver illness, a process known as staging.
- Assist in creating treatment regimens based on the liver's condition.
- Evaluate the efficacy of treatment for liver illness.
- Liver monitoring following a liver transplant.
Your doctor may instruct you to have a liver biopsy if you have:
- Unexplained abnormal liver test results.
- A lump (tumor) or other abnormality in the liver as seen on imaging tests.
- Persistent fever.
A liver biopsy may also be done to help diagnose and often stage-specific liver diseases, including:
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Chronic hepatitis A and B.
- Immune hepatitis.
- Alcoholic liver disease.
- Primary biliary cirrhosis.
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis.
- Hemochromatosis.
- Wilson's disease.
The risks of a liver biopsy
A liver biopsy is a safe technique if performed by a qualified doctor. Potential risks include:
- Pain
The most frequent side effect following a liver biopsy is pain at the biopsy site. Usually, there is relatively minor discomfort following a liver biopsy. If the pain is unbearable, narcotic painkillers may be prescribed, such as acetaminophen with codeine (Tylenol with codeine).
- Bleeding
Following a liver biopsy, bleeding could happen. If you have significant bleeding, you might need to be hospitalized for a blood transfusion or surgery to control the bleeding.
- Infection
Bacteria can sporadically infiltrate the bloodstream or the abdominal cavity. In rare cases, the needle may prick another internal organ, such as the gallbladder or lung, during the liver biopsy.
Transjugular liver biopsy in Istanbul
A thin tube is inserted into a large vein in your neck, then threaded through a vein that passes through your liver. If you have had a transjugular liver biopsy, other uncommon risks may include:
- Hematoma in the neck
- Blood may collect around the area where the catheter was inserted, which can cause pain and swelling
- Problems with the nerves in the face
Rarely, a transjugular liver biopsy can damage nerves and affect the face and eyes, causing short-term problems, such as:
- Ptosis
- Temporary sound problems
- Your voice may become hoarse or weak, or you may lose your voice for a short time
- A hole in the lung
If the needle accidentally punctures the lung, it may collapse (pneumothorax).
Share this page






