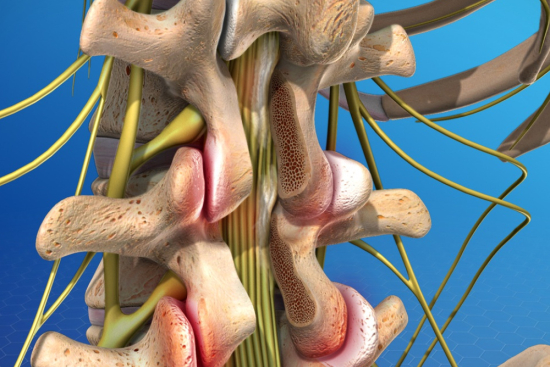
Laminectomy, a surgical decompression procedure, is used to relieve compression of the spinal cord or roots.
This technique involves removing part of the vertebra's posterior arch to widen the spinal canal and release compressed nerve structures.
Laminectomy: Cost of surgery in Turkey
Do you have chronic back pain? Choose laminectomy in Turkey and regain your quality of life. Benefit from personalised care: free teleconsultation and quote, experienced surgeons, modern clinics and an all-inclusive stay.
The cost of a laminectomy in Turkey is estimated from 6,000 Dollars.
Benefit from Turkey's world-renowned reputation for spine surgery and an attractive cost for a quality operation.
Thousands of satisfied patients testify to our expertise. Entrust your health to us and choose excellence.