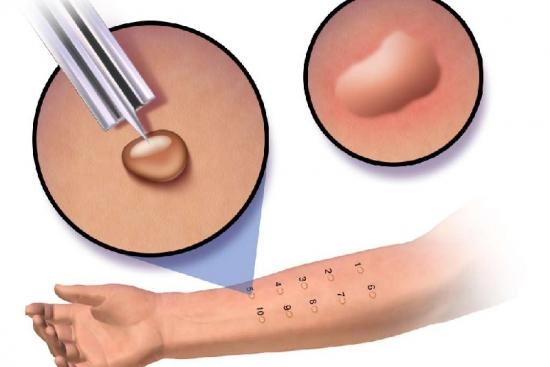
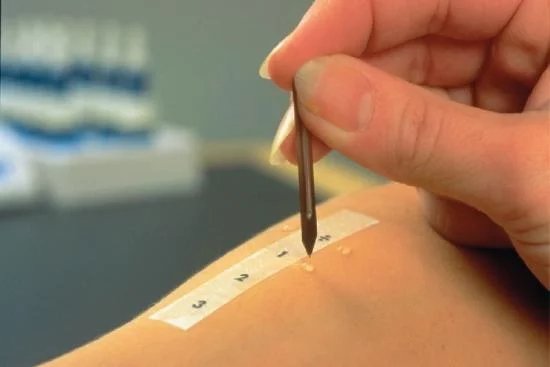
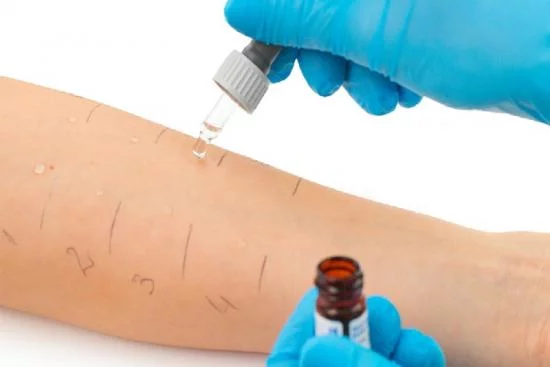
Increasingly, food intolerances manifest as digestive symptoms, often caused by intestinal irritation. Although they are similar to those of a food allergy, they differ in the absence of an immune response. Nevertheless, as with allergies, the management of food intolerance involves the more or less strict elimination of certain foods from the diet.