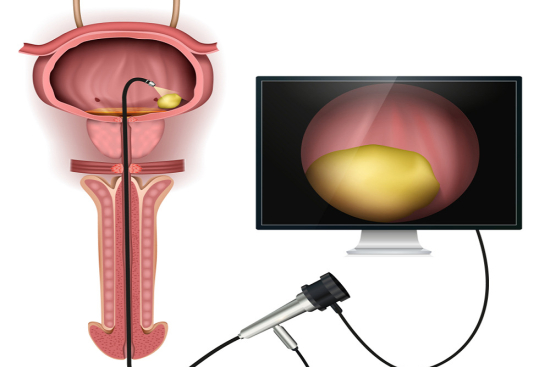
Cystoscopy is an endoscopic procedure that provides direct visualization of the bladder and urethra. Using a cystoscope, a thin, flexible instrument equipped with a light source and camera, the physician can examine the bladder and urethral lining in detail. This examination is indicated for the diagnosis and evaluation of various urological pathologies, including recurrent urinary tract infections, hematuria (blood in the urine),tumors, and urinary stones.
Cost of cystoscopy in Turkey
The cost of a cystoscopy in Turkey is estimated to be between 1,350 and 1,650 Euros. This can vary depending on the diagnosis made, the medical facilities chosen and any additional treatments required.
Benefit from personalized care in modern clinics with state-of-the-art equipment.
Ready to learn more? Contact us now for a free consultation and personalized quote.