Opening the skull, which is necessary for certain neurosurgeries, exposes the brain to the risk of infection. To limit this risk and facilitate surgery, a portion of the bone is often temporarily removed. This procedure, known as a craniectomy, allows easier access to the brain and facilitates drainage.
To restore the integrity of the skull and protect the brain, a cranioplasty is usually scheduled a few months later. This involves reconstructing the missing bone with a biocompatible material.
- Patients who have undergone craniectotomy.
- Craniectomy.
- Between 1 and 2 hours.
- Hospital stay of 4 to 10 days.
- Resumption of normal activities within 6 to 8 weeks.
Cranioplasty: Price and coverage in Turkey
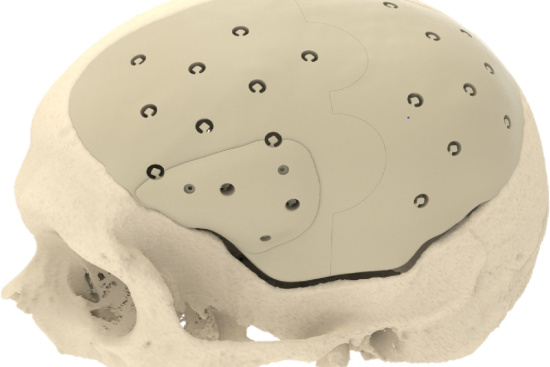
Thanks to remarkable technological advances, including 3D printing and computer-assisted surgery, our partner surgeons in Turkey are able to provide you with customized, high-precision solutions for bone reconstruction.
The materials used, such as bioactive ceramics and polymer composites, promote optimal bone integration and accelerate healing.
Our partner clinics also offer a modern, welcoming environment with highly qualified medical teams.
The price of a cranioplasty in Turkey ranges from $6,300 to $7,700.
When you choose Turquie Santé for your cranioplasty, you're choosing recognized expertise, cutting-edge technology and personalized care, all at an attractive price.
Best Clinics with Verified Reviews

- Multispecialized hospital
- 7 operating rooms
- Capacity é of 170 beds

- Multispecialized hospital
- Hospital founded in 2007
- Very good reputation in ENT department
What is cranioplasty?
Cranioplasty is a surgical procedure used to reconstruct the skull when it is damaged or deformed. Such damage can be caused by accidents, disease, or birth defects.
First documented in ancient times, this surgical technique has evolved significantly over the centuries. Today, it offers remarkable aesthetic and functional results.
Beyond aesthetics: the multiple benefits of cranioplasty
Beyond simple bone repair, cranioplasty requires careful planning and advanced technical expertise. By restoring the integrity of the cranial cavity, cranioplasty provides multiple benefits to the patient:
- Increased protection.
- Accelerated recovery.
- Restored well-being.
- Potential benefits to brain function.
Main indications for cranioplasty
Cranioplasty is a surgical procedure indicated in several situations:
- After head trauma: Fractures or loss of bone after a blow may expose the brain and require bone reconstruction.
- After neurosurgery: Craniectomies performed to gain access to the brain create defects that must be filled to protect the brain and restore skull structure.
- For congenital deformities: Abnormalities of cranial shape or structure present at birth can be surgically corrected to improve the appearance and function of the brain.
- For aesthetic reasons: In some cases, cranioplasty is performed to correct minor defects that affect a patient's self-esteem.
Preoperative evaluation of cranioplasty
Before proceeding with cranioplasty in Turkey, a thorough clinical examination of the skull defect, surrounding tissues, and search for infectious or neurological signs is essential.
Additional tests are also necessary:
- Medical imaging (CT, MRI) to visualize bone and soft tissue.
- A complete neurological examination to assess cognitive, motor and sensory function.
Finally, a detailed medical history, including head injuries, previous surgeries, comorbidities and current treatments, allows for an accurate diagnosis and optimal planning of the procedure.
Materials used in cranioplasty in Türkiye
Reconstructing the skull during cranioplasty is a critical step that requires careful material selection. This choice depends on many factors, such as the extent and location of the lesion to be filled, the patient's general health, and his or her expectations for the aesthetic result.
Natural bone grafts
Natural bone grafts used in cranioplasty include:
- Autografts: Harvested from the patient's own bone (iliac crest, calvarium),they offer perfect biocompatibility and optimal bone integration. However, they require additional surgery and the amount of tissue available may be limited.
- Allografts: Derived from deceased donors, they are more readily available but carry a low risk of rejection and disease transmission.
Synthetic materials
Synthetic materials include:
- Metals: Titanium (or titanium alloys) is highly biocompatible and durable, allowing for customized reconstruction. However, it can interfere with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans.
- Polymers: Polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA),which is easily molded and radiolucent, is an interesting option. However, it is less resistant than bone and may increase the risk of infection.
- Ceramics: Hydroxyapatite, which is biocompatible and promotes bone growth, is a promising alternative. However, its fragility limits its use.
In Turkey, the choice of the ideal material is a complex decision that must be made on a case-by-case basis, carefully weighing the advantages and disadvantages of each option.
Process of skull reconstruction in Turkey
Cranioplasty is a surgical procedure used to reconstruct a damaged part of the skull, often following trauma or neurosurgery.
Performed under general anesthesia, an incision is made in the scalp to gain access to the damaged area. The surgeon then places a bone implant that is customized to the shape of the patient's skull to fill the defect. The implant can be autologous (from the patient),allogeneic (from a donor),or synthetic.
Once firmly in place, the incision is closed and a bandage is applied. This delicate procedure requires a high degree of surgical expertise to ensure optimal aesthetic and functional results.
Postoperative care after cranioplasty
Postoperative care plays a critical role in the success of cranioplasty. It includes:
In-hospital monitoring
Medical teams continuously monitor the patient's vital signs (blood pressure, heart rate, breathing) and neurological status.
Regular examinations are also performed to detect any signs of infection, bleeding, or other problems.
Medical treatment
Medications are prescribed to relieve postoperative pain.
Antibiotics are often given to prevent the risk of infection.
Rehabilitation
Gentle, specific exercises are recommended to prevent stiffness, improve circulation, and strengthen muscles.
In the case of neurological deficits, appropriate re-education is provided.
Regular follow-up
Regular consultations are held to monitor healing, the condition of the graft or implant, and the patient's neurological status. In addition, imaging studies (CT, MRI) may be performed to verify the correct position of the graft and to detect any complications.
Possible complications after cranioplasty
Although cranioplasty is generally a safe procedure, as with any surgical procedure, there is a risk of complications:
- Risk of infection: Infection can occur at the surgical wound or deeper in contact with the brain. Signs of infection may include redness, warmth, swelling of the operated area, fever, purulent discharge, and sharp pain.
- Problems with the graft or implant: The graft or implant may move out of place. In rare cases, the body may reject the implanted material. In some cases, the material may cause infection. In addition, the graft or implant may fracture, especially after trauma.
- Hematoma: Internal bleeding can increase intracranial pressure and cause symptoms such as swelling at the wound site, severe pain, headache, nausea, and vomiting.
- Neurological complications: Due to the proximity of the brain, disorders of consciousness, paralysis, numbness, speech disorders, or seizures may occur.
- Other: Less commonly, cerebrospinal fluid leakage, nerve damage, or allergic reactions may occur.
Most patients in Turkey do not experience major complications after cranioplasty. However, it is important to report any unusual signs, even minor ones, to your doctor immediately.
Share this page