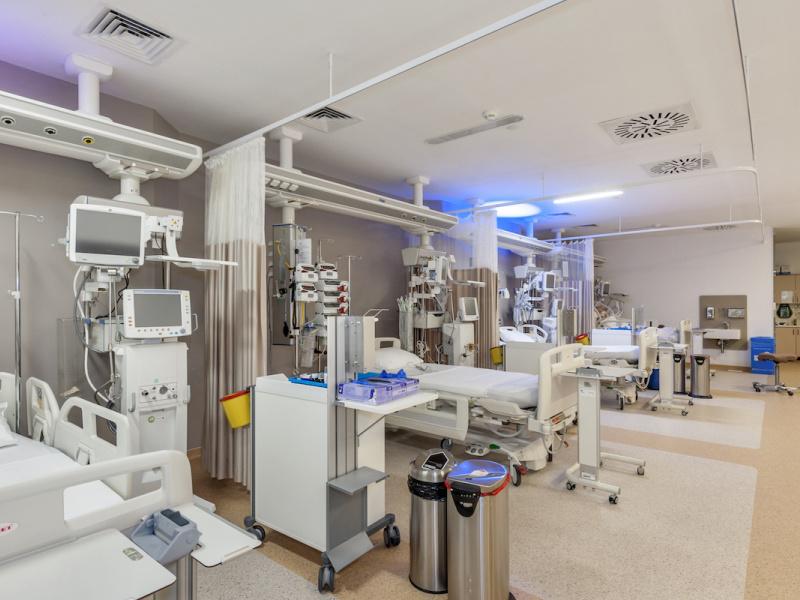
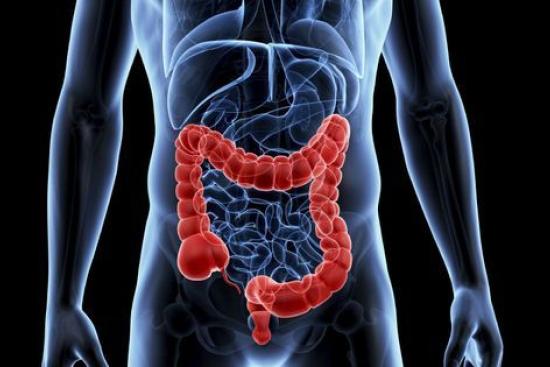
Colorectal cancer is one of the most common cancers worldwide, affecting the colon or rectum and often developing silently in its early stages. Early detection is key, as timely diagnosis dramatically improves treatment success and long-term outcomes.
In Turkey, patients can access advanced colorectal cancer treatments in modern, internationally accredited hospitals, where experienced oncologists and surgical teams provide personalized, multidisciplinary care to maximize recovery and quality of life.
Colorectal cancer treatment in Turkey: Expertise & competitive prices
In Turkey, the average cost of complete colorectal cancer treatment ranges from $7,020 to $14,040 USD, depending on the treatment protocol.
Turquie Santé provides full support throughout your medical journey, including:
- Free and fast personalized quote
- Assistance with medical visa
- Airport-to-hospital transfers
- Remote post-treatment follow-up
Book your free teleconsultation and begin your colorectal cancer treatment in Turkey with confidence and expert care.