Brain tumors, which can affect different parts of the brain, are a major public health problem today. These growths, which result from the uncontrolled proliferation of cells, can be benign (slow-growing and non-invasive) or malignant (fast-growing and invasive).
Among the most common and feared brain tumors is brain cancer. This type of tumor affects a significant number of people worldwide and represents a major challenge for medical research.
Best Clinics with Verified Reviews

- Multispecialized hospital
- 7 operating rooms
- Capacity é of 170 beds
Causes of brain cancer
Although researchers have conducted numerous studies, the exact causes of brain cancer remain a mystery. However, several factors may increase the risk of developing this tumor, including:
- Exposure to ionizing radiation: This includes radiation therapy to treat other cancers and exposure to natural radiation from the environment.
- Immunosuppressive treatments: These drugs, used to treat diseases such as HIV/AIDS, weaken the immune system, making it more susceptible to infection and cancer.
- Excessive cell phone use: Recent research suggests that prolonged use of cell phones, especially by children, may increase the risk of brain tumors.
- Exposure to vinyl chloride: This chemical, found in certain materials and industrial products, is classified as a carcinogen by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC).
Symptoms of a brain tumor
Brain and spinal tumors can present with a variety of symptoms, depending on their location and whether they are benign or malignant.
In general, clinical signs only appear at an advanced stage, when the tumor has grown large enough to affect the function of the brain or spinal cord.
The most common symptoms of a brain tumor are:
- Headache: Frequent, often worse in the morning or with exertion.
- Memory problems: Frequent forgetfulness, difficulty remembering events or people.
- Vision problems: blurred or double vision, or loss of visual field.
- Epileptic seizures: sudden, uncontrolled seizures.
- Abnormal movements: Shaking, clumsiness, lack of coordination.
- Speech disorders: Difficulty speaking, finding words, or understanding speech.
- Loss of balance: dizziness, staggering, frequent falls.
- Coma: prolonged loss of consciousness.
- Fine motor problems: Difficulty writing, handling fine objects.
- Difficulty swallowing: choking, regurgitation.
You should seek immediate medical attention if you experience one or more of these symptoms.
Early diagnosis is critical for effective treatment of brain and spinal tumors.
Diagnosis of brain tumors
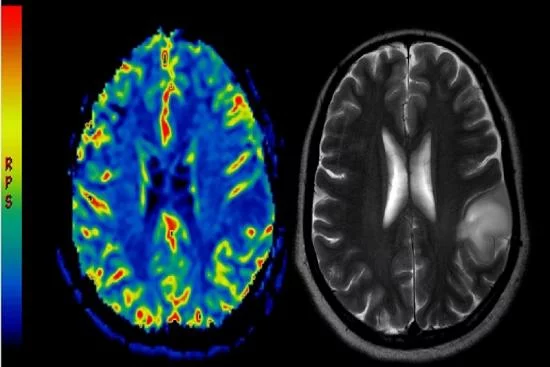
In Turkey, we generally use two types of imaging tests to diagnose brain tumors:
- Pet-Scan, which has proven to be effective in detecting 85% of tumors, is a useful tool that allows physicians to confirm the presence, location, and size of tumors.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is used to identify tumors not detected by Pet-Scan. In practice, the MRI procedure is similar to a CT scan, but uses an electromagnetic field instead of radiation.
Treatment of brain tumors
Brain cancer treatment in Turkey is a complex and personalized process that combines different therapeutic options to optimize the chances of cure and preserve the patient's quality of life. Ongoing advances in oncology research in Turkey are helping to refine therapeutic strategies. More effective and less toxic alternatives are now available to our patients.
The main treatments used in the treatment of brain tumors are:
Surgical treatment
Surgery is often the first step in treatment with the goal of removing all or part of the tumor. The feasibility of surgery depends on the location and size of the tumor. Surgical techniques include
- Craniotomy: Access to the brain through an opening in the skull.
- Cerebral mapping: Use of electrical currents to identify functional areas of the brain and minimize neurological risks during surgery.
- Cerebrospinal fluid drainage: Drainage of excess cerebrospinal fluid accumulated by the tumor to relieve intracranial pressure.
Chemotherapy: Fighting cancer cells
Chemotherapy uses powerful drugs to destroy cancer cells. It can be given intravenously or orally and is often used in combination with radiation therapy or for recurrence after surgery.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy uses beams of X-rays or other charged particles to target and destroy cancer cells. It may be used before surgery to reduce the size of the tumor, after surgery to eliminate residual cells, or in the event of a recurrence.
Immunotherapy approach
Immunotherapy stimulates a patient's immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. This promising approach uses drugs or biological agents to activate immune cells or block the mechanisms that prevent the immune system from recognizing cancer.
Targeted therapy
Targeted therapy specifically attacks the molecular abnormalities present in cancer cells, thereby limiting damage to healthy cells. This approach uses drugs that block specific signaling pathways or inhibit the growth and division of cancer cells.
Terminal brain cancer: Chances of survival
The terminal phase of brain cancer represents the last stage of the disease when curative treatment is no longer an option. This period is characterized by the patient's great fragility, both physically and psychologically. The main objective is to alleviate suffering and accompany the patient in his last moments.
Before reaching this stage, the physician assesses how far the cancer has progressed and how well the treatment can cope with it. Based on this analysis, the oncologist provides a prognosis for the patient's chances of survival.
This prognosis takes into account several key factors:
- Tumor grade: The higher the tumor grade, the more aggressive and advanced the cancer.
- Type of tumor.
- The patient's age.
- Tumor size and location: A small tumor located in a surgically accessible area is more favorable than a large, difficult-to-access tumor.
- Chromosomal abnormalities: Certain chromosomal abnormalities may affect tumor behavior and response to treatment.
Accompaniment and palliative care
The terminal phase of brain cancer is a difficult and upsetting time. However, it does not have to mean suffering and abandonment. With quality medical and human care, it is possible to guide patients through a serene transition, surrounded by their loved ones.
During this phase, the relief of pain and other physical symptoms becomes a priority. Palliative care, provided by our multidisciplinary team in Turkey, plays an essential role in the care of patients and their families. We provide physical, psychological, emotional and spiritual support to help them cope with this difficult time.
Supporting our patients also includes open, caring communication. We respect our patients' wishes and involve them in decisions about their care.
Share this page
- Gliomas: or glial tumors, which originate from the cells of the glia representing up to 90% of the nervous system.
- Glioblastoma: this is the most common brain cancer, it results from an abnormal proliferation of astrocytes (cells of the central nervous system).
- Meningioma: a tumor that is caused by the abnormal proliferation of the meninges (cells surrounding the brain and spinal cord).
- Medulloblastoma: the second most common cancer in children, the exact cause of this tumor is not yet known.
- Pituitary Adenomas: a benign tumor that develops in the pituitary gland. This gland is located at the base of the brain and is responsible for the secretion of several hormones.
- Brain Lymphoma: a rare form of tumor resulting from the abnormal proliferation of B lymphocytes in the brain.
Some known risk factors for brain cancer include:
- Radiation exposure of the head
- Immunodeficiency: weakness of the immune system resulting from a disease, such as AIDS, or from taking certain immunosuppressive medicines
- Contact with vinyl chloride: chemical used in the manufacture of plastic.
There are signs that show you may have a brain tumor:
- Severe headaches upon waking up
- Epileptic seizures
- Vomiting and nausea
- Personality, mood or behavior disorders
- Difficulty communicating or deciphering words
- Involuntary movements or difficulty walking (adynamia)
- Asthenia (general or one side weakness).
The main treatment for brain tumors in our partner clinics in Turkey is surgery. Radiotherapy or chemotherapy is used before and after the procedure to shrink the size of the tumor or remove cancer cells that are left in the brain.
Targeted therapy and immunotherapy have also become essential in the treatment of cancer.