Brain hemorrhage: What is it?
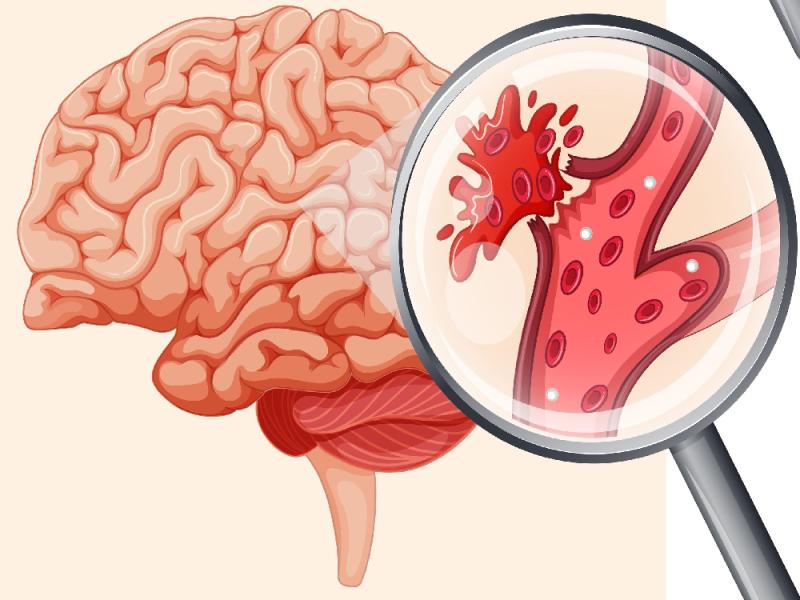
A brain hemorrhage, also known as a brain bleed, occurs when a blood vessel inside the skull suddenly bursts. This bleeding leads to the formation of a hematoma, a blood clot that puts increasing pressure on the brain tissue.
The rigidity of the skull prevents the clot from expanding, compressing vital brain structures.
This compression reduces the brain's blood supply, depriving nerve cells of the oxygen they need to function. Without adequate oxygen, brain cells can quickly die, causing irreversible, life-threatening damage. The consequences can be varied and severe, ranging from neurological disorders to coma and even death.
Symptoms & warning signs of brain bleeding
A brain bleed is usually characterized by a severe headache, often accompanied by vomiting.
However, other symptoms may occur, depending primarily on the location of the brain hematoma.
These include:
- Altered consciousness, ranging from stupor to coma.
- Motor disorders: paralysis on one side of the body (hemiplegia), incoordination and clumsiness.
- Sensory disorders: numbness, tingling, paresthesia.
- Speech disorders (aphasia).
- Visual disturbances: double vision, visual field disturbances.
- Dizziness and instability.
- Stiff neck, often associated with severe headache.
Causes of internal brain bleeding
The most common causes of intracerebral hemorrhage are:
- High blood pressure (hypertension): Chronic high blood pressure weakens the walls of the brain vessels, making them more likely to rupture.
- Head trauma: Violent blows to the head can cause vascular damage and bleeding.
- Cerebral vascular malformations: Congenital abnormalities of the blood vessels in the brain can increase the risk of rupture.
- Coagulation disorders: Problems with blood clotting may increase the risk of brain bleeding, especially when taking anticoagulants.
- Brain tumors: Some brain tumors can cause bleeding by compressing or invading blood vessels.
Other risk factors, such as advanced age, alcoholism, drug use, diabetes, and the use of certain medications, can also increase susceptibility to cerebral hemorrhage.
Types of brain bleeds
A brain hemorrhage occurs when a blood vessel inside the skull ruptures, causing bleeding. There are several types of bleeding, depending on the location of the hemorrhage:
- Intracerebral hemorrhage: Intracerebral hemorrhage is an effusion of blood within the brain tissue. It is often caused by the rupture of a blood vessel and is a form of hemorrhagic stroke.
- Epidural hemorrhage: Blood accumulates between the dura mater (the brain's outer membrane) and the skull bone. It is usually caused by head trauma, such as a blow to the head.
- Subdural hemorrhage: Bleeding occurs between the dura mater and the arachnoid membrane (second brain membrane). This is also often associated with head trauma.
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage: Blood leaks into the space between the arachnoid membrane and the dura mater (inner membrane of the brain). It is often caused by a ruptured aneurysm or head trauma. Typical symptoms are sudden, severe headaches, often described as "the worst pain of my life".
- Intraventricular hemorrhage: Bleeding into the brain's ventricles (cavities filled with cerebrospinal fluid). This is a rarer form that is often associated with other types of bleeding. Symptoms are similar to other types of hemorrhage, but may include altered consciousness and seizures..
Management of cerebral hemorrhage
A brain hemorrhage is a medical emergency that requires immediate attention. The consequences can be serious, ranging from permanent neurological damage to death. Treatment of a brain bleed depends on the type, location, and extent of the bleed. It may include:
- Surgery: To remove the accumulated blood and repair the damaged vessel.
- Medication: To control blood pressure, reduce brain edema, and prevent seizures.
- Supportive care: To maintain vital functions and prevent complications.