What is amblyopia?
The term amblyopia indicates a condition of reduced or absent vision that occurs in only one eye, or more rarely in both eyes. This ocular discomfort develops at pediatric age.
The problem stems from incorrect or delayed nerve and optical development. It consists of a deficit of the visual apparatus: the brain, failing to correctly interpret the information that reaches it, deactivates - partially or totally - the signals coming from one of the two eyes. In children, the damage is generally reversible, in principle up to 4-6 years.
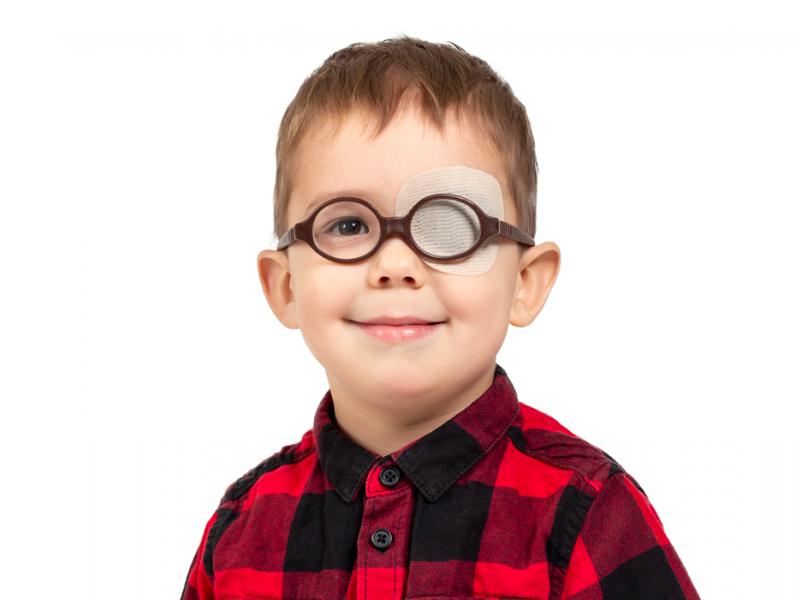
It is often called "lazy eye", to emphasize the presence of a stronger eye (which functions well) and a weaker eye, but it is important to emphasize that the adjective lazy in no way denotes a possible character trait of the patient. And only refers to the need to force the brain to reestablish a correct connection with the affected eye.
Types of lazy eye
Generally, amblyopia can be classified into two types:
- Functional amblyopia: this is the most common type, related to a learning disability of binocular vision (the synchronized use of both eyes) during childhood. It is independent of any visual pathway disease, but rather related to a refractive disorder.
- Organic amblyopia: this is the form linked to a pathology of the eye, for example, unilateral congenital cataract, or ptosis (drooping eyelid).
The causes of amblyopia
The amblyopic eye, unstimulated, is the result of several factors:
- Strabismus: also called eye misalignment, it causes amblyopia in about 70% of cases due to the loss of parallelism of gaze and the non-alignment of the two eyeballs.
- Astigmatism: it is a deformation in the curvature form of the cornea with which the subject cannot see clearly, which favors the development of amblyopia.
- Myopia: consists of difficulty in seeing images from a long distance.
- A physical disorder: ptosis, a congenital cataract (loss of transparency of the natural lens of the eye).
The symptoms of lazy eye
The symptoms of reached by the lazy eye are multiple, we can classify them according to the individual age :
In children
Rarely that children complain about a physical disorder that bothers them and especially when it occurs during early childhood (before 6 years).
Therefore, it is very important to proceed to a screening to catch up and treat lazy eye before it develops and remains irreversible.
Nevertheless, we can detect some gestures that signal the presence of an ocular problem, such as blinking of one eye, in particular, rubbing of one of the eyes, and headaches.
In adults
Lazy eye, which has not been taken care of from childhood, can develop to lead to a loss of acuity in a major subject.
There are 3 levels of amblyopia: mild, moderate, and profound.
Diagnosis methods
Screening is the type of testing needed for diagnosis in the case of visual disturbances. This diagnosis is based on an evaluation of visual acuity.
For children who cannot express themselves, a pupillary reflex analysis, applied by photo-screening, is strongly recommended.
Amblyopia treatment
The earlier the treatment is carried out, the better will be the result. This explains why the success rate is estimated at 99% when treatment is performed before the age of 2 and 90% before the age of 6.
The treatment is based on stimulating the lazy eye by :
- Hiding the unaffected eye: that’s called occlusion of the valid eye
- Wearing glasses or contact lenses
- Correction of strabismus
- Treatment of cataracts
If the correction of refraction by wearing contact lenses or glasses is impossible, an application of eye drops on the healthy eye will inhibit it to stimulate the amblyopic eye to work.
Prevention of lazy eye
To prevent the development of amblyopia, regular monitoring of your child's vision by a practitioner is mandatory. The follow-up decreases the chance of anomaly aggravation.