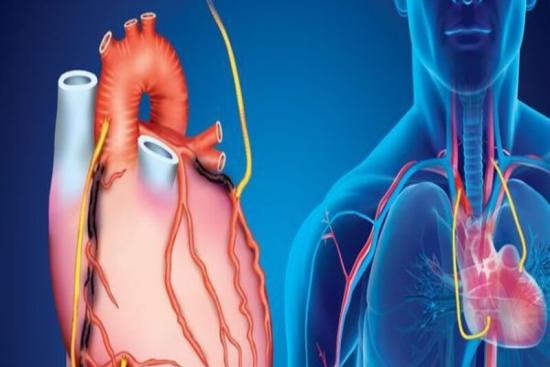
Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG),commonly referred to as bypass surgery, is designed to increase blood flow to the heart muscle by bypassing blocked or narrowed coronary arteries. This procedure requires the use of vessels from other areas of the body to create alternative blood flow paths. By bypassing blockages, it restores normal blood flow to the heart.
Discover the most affordable cost for Coronary artery bypass grafting in Turkey. Get a personalized and free quote from our trusted partner clinics.
- Inflammatory reactivity
- Infection
- Stroke
- Pneumonia
- The operation lasts between 3 to 6 hours
Heart bypass surgery CABG cost in Turkey
Turquie Santé connects you with specialized hospitals for heart bypass surgery and CABG procedures in Istanbul, Turkey. Through our platform, you can easily request a quote online in one click.
Cardiology is one of the most advanced medical specialties in Turkey. Our partner clinics and hospitals are top-notch and have exceptionally qualified staff.
What's more, the cost of healthcare doesn't always correlate with its safety. Affordable medical care that meets international quality standards is available.
The cost of CABG surgery in Istanbul, Turkey may vary depending on factors such as the patient's age and the number of blood vessels being transplanted. Rest assured that we are committed to offering the most competitive prices.
In addition, some private health insurance plans may cover this surgery. It's a good idea to check with your insurance company if you're considering coronary artery bypass graft surgery.
Best Clinics with Verified Reviews

- Multispecialized hospital
- 7 operating rooms
- Capacity é of 170 beds

- Multispecialized hospital
- Hospital founded in 2007
- Very good reputation in ENT department
Understanding Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting
CABG is a surgical procedure designed to divert blood around a segment of an obstructed or partially blocked artery in the heart. This is done by grafting a piece of healthy blood vessel from another part of the body to the coronary artery. CABG is a major operation, but it can be a life-saving treatment for people with severe coronary artery disease (CAD).
It's important to distinguish this procedure from coronary angioplasty, which targets coronary atherosclerosis, a specific heart condition. Nonetheless, both interventions play a substantial role in enhancing the cardiovascular system and the overall quality of life for patients by increasing blood flow to the heart muscle.
Indications for Coronary Artery Bypass Graft
CABG is indicated for people with:
- Significant blockages in the left main coronary artery, which supplies blood to the left ventricle, the main pumping chamber of the heart. A blockage in this artery may lead to a heart attack.
- Three-vessel disease: This means that there are significant blockages in three of the four major coronary arteries. Three-vessel disease can severely restrict blood flow to the heart and increase the risk of a heart attack.
- Two-vessel disease with proximal left anterior descending (LAD) artery involvement. The LAD artery is the most important coronary artery. A blockage in the proximal LAD artery may increase the risk of a heart attack.
- Severe angina, characterized by persistent chest pain unresponsive to medication or other therapies, is a symptom of CAD. This occurs when the heart muscle doesn't receive adequate blood supply. In cases where angina remains severe and doesn't improve with other treatments, CABG might be considered as a therapeutic option.
- Recurrent heart attacks: If you have had multiple heart attacks, CABG may be an option to prevent future heart attacks.
CABG is not always the best treatment for CAD. In some cases, other treatments in Türkiye, such as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI),may be more appropriate. PCI is a less invasive procedure that uses a catheter to open up a blocked coronary artery.
The decision of whether or not to have CABG should be made by you and your doctor after careful consideration of your circumstances.
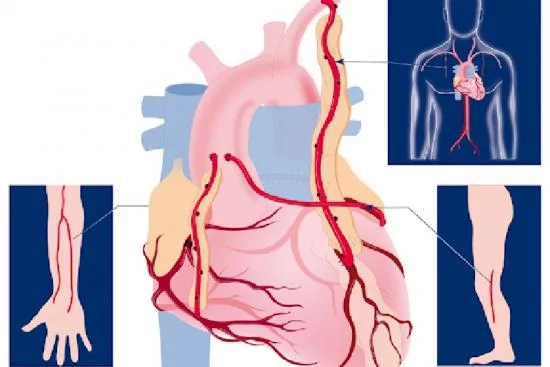
CABG procedure steps
In general, coronary artery bypass graft surgery takes between 3 and 6 hours under general anesthesia.
Pre-operative Preparation
The coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) procedure involves several steps. First, preoperative preparation is performed, involving the administration of general anesthesia to keep the patient asleep and pain-free during surgery. Next, a vertical incision is made in the center of the chest to expose the heart. At the same time, a healthy blood vessel from another part of the body, such as the leg or chest, is harvested and prepared for use as an arterial graft.
During the surgery
During surgery, the patient is connected to a heart-lung bypass machine. This machine takes over the functions of the heart and lungs.
Next, the harvested graft is attached to the blocked coronary artery, creating a new path for blood flow.
Once the grafts are in place, the heart-lung machine is disconnected and the heart can resume normal function. Finally, the chest incision is closed with sutures or staples.
Post-operative Care
After surgery, patients are usually admitted for a few days to an intensive care unit for recovery and careful monitoring. They will receive analgesics to manage any post-operative pain. Respiratory therapy may be undertaken to promote lung clarity and reduce the risk of complications. In addition, a cardiac rehabilitation program including exercise, counseling, and educational information is offered to support patients in their post-surgical recovery and improve their heart health.
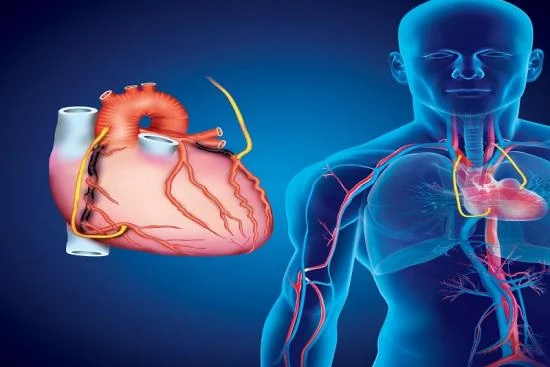
CABG surgery complications and effects
After surgery, you may experience fatigue and discomfort during the first few weeks of recovery. There may be moments of intense, temporary pain on both sides of your chest.
Short-term effects
You may experience pain in your chest, shoulders, and upper back. The incision site on your chest and the area where a healthy vein was taken may feel tender or swollen.
Medium-term effects
After CABG heart surgery, several complications may occur in the medium term:
- Increased inflammatory reactivity
- Increased blood pressure
- Risk of infection
- Possibility of heart attack, heart failure, or stroke
- Pneumopathy
Long-term effects
Some people may report memory problems, but these usually don't get worse over time. Other potential risks include:
- Irregular heart rhythm
- Possible graft rejection
- Difficulty breathing
These effects can range from severe to moderate, and temporary to long-term. Their impact is influenced by your initial medical condition, so it's important to discuss any concerns with your cardiologist.
Share this page