Turquie Santé: Your partner in medical excellence
Turkey is an inevitable choice for those considering medical treatment abroad. With its state-of-the-art facilities, highly qualified medical professionals, and advanced treatments, Turkey has positioned itself as a top choice for medical tourism.
The country boasts internationally accredited hospitals and clinics that guarantee strict quality standards. In addition, the country's healthcare infrastructure is complemented by a wide range of specialties covering various fields.
When it comes to healthcare services in Turkey, patients can feel confident in the hands of highly qualified medical professionals who put the well-being and individual needs of each patient first.
Plan your medical stay with Turquie Santé
Turquie Santé is committed to providing you with medical and aesthetic treatments from the best partner clinics and hospitals throughout Turkey.
As a leader in the medical tourism industry, Turquie Santé has built a solid reputation for providing exemplary healthcare in Turkey. With an extensive network of certified clinics and hospitals, Turquie Santé ensures that its patients receive the highest level of care and the most effective treatments available.
In addition to escorts, we provide interpreters to ensure good communication with doctors. This enables hospital staff to respond to requests from patients who speak different languages.
Explore Aesthetic and Medical Treatments in Turkey
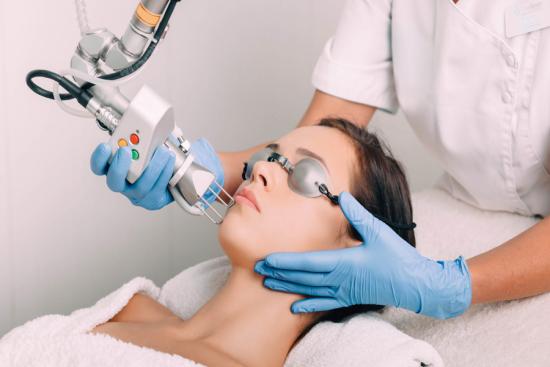
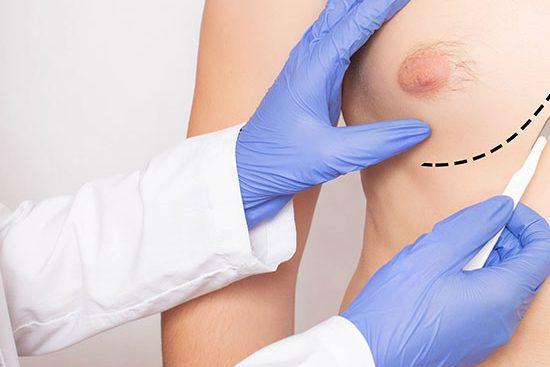
Turkey's reputation as a hub for aesthetic treatments has grown steadily over the years. From breast augmentation and liposuction to facelifts and rhinoplasty, Turquie Santé offers a range of cosmetic solutions tailored to the unique needs of each individual. The use of innovative techniques and advanced technologies guarantees natural results with minimal recovery time.
Turquie Santé also offers a comprehensive range of medical treatments covering a variety of specialties. From orthopedics and cardiology to neurology and oncology, Turquie Santé's medical experts address a wide range of health concerns.
With a focus on patient-centered care, Turquie Santé guarantees accurate diagnoses, personalized treatment plans, and superior care. The use of advanced medical equipment and techniques ensures positive outcomes and a better quality of life for patients.

 Package
Package