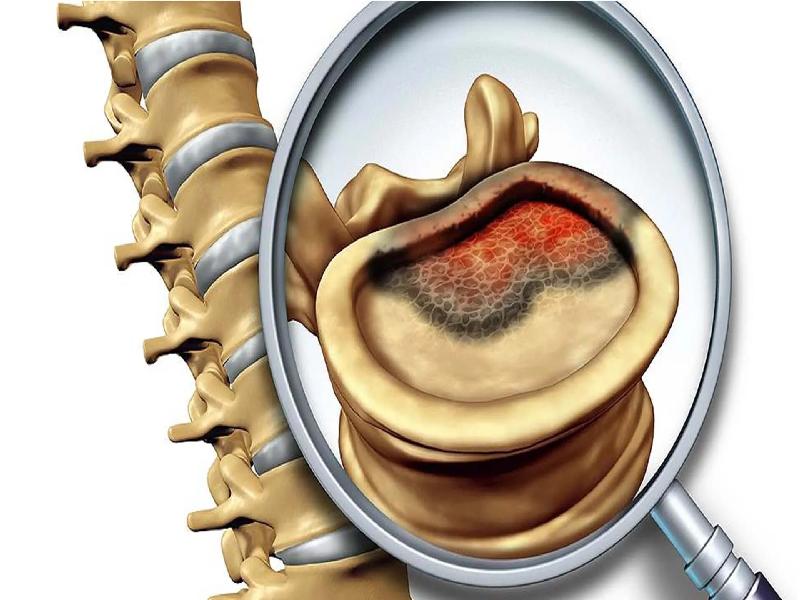
Facing a diagnosis of a bone tumor or a lesion within the bone marrow can be deeply unsettling. Uncertainty, fear, and questions about treatment options often come hand in hand. For many patients, the idea of traditional open surgery, along with its risks and long recovery, only adds to the stress. But what if it were possible to precisely target and destroy abnormal tissue through a minimally invasive approach, using nothing more than a tiny incision?
This advanced, patient-focused approach is routinely performed in specialized interventional radiology and oncology partner centers in Turkey, combining expertise, cutting-edge technology, and personalized care.