3D bioprinting represents a major breakthrough in the field of regenerative medicine in Turkey. This innovative technology enables the design of functional biological tissues and organs created from living cells and biomaterials. It opens up unprecedented prospects in the treatment of severe skin lesions by providing customized grafting solutions. It is also a valuable tool for biomedical research, providing more realistic in vitro models.
Patients suffering from :
- Severe skin lesions.
- Burns.
- Dermatological diseases.
- Risk of immunological rejection.
- Infection.
- Poor tissue integration.
- Adverse reactions to biomaterials.
- Skin grafting.
- Cell Therapy.
- Growth factor therapy.
- Tissue engineering therapy.
Best Clinics with Verified Reviews

- Multispecialized hospital
- 7 operating rooms
- Capacity é of 170 beds

- Multispecialized hospital
- Hospital founded in 2007
- Very good reputation in ENT department
3D Bioprinting: What is it?
The skin, a vital organ, can be severely damaged by traumatic events. Current treatments, while necessary, do not always meet patient needs in terms of graft quality and availability.
3D bioprinting offers an innovative solution, making it possible to produce bioprinted skin tissue that is perfectly tailored to each individual patient. This cutting-edge technology paves the way for personalized regenerative medicine and offers new hope to people suffering from extensive skin damage.
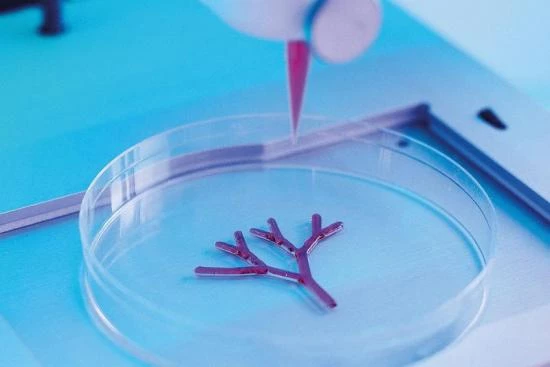
The bioprinting process
Bioprinting relies on cells' ability to organize and proliferate within an artificial extracellular matrix. The cells used are typically derived from the tissue to be regenerated (autologous) or from a compatible donor (allogeneic). They are combined with biomaterials such as hydrogels, bio-inks, or biofilms that provide structural support and a favorable environment for cell growth.
Bioprinting follows a rigorous multistep protocol:
- Data Acquisition: A three-dimensional image of the area to be reconstructed is obtained using medical imaging techniques such as MRI or computed tomography (CT).
- Preparation of biomaterials and cells: Cells are grown in the laboratory and biomaterials are prepared to ensure biological compatibility.
- Bioprinting: Cells and biomaterials are deposited on a 3D printing platform, precisely and controlled based on previously acquired data.
- Maturing: The bioprinted tissue is placed in a controlled environment to allow the cells to organize, proliferate, and form functional tissue.
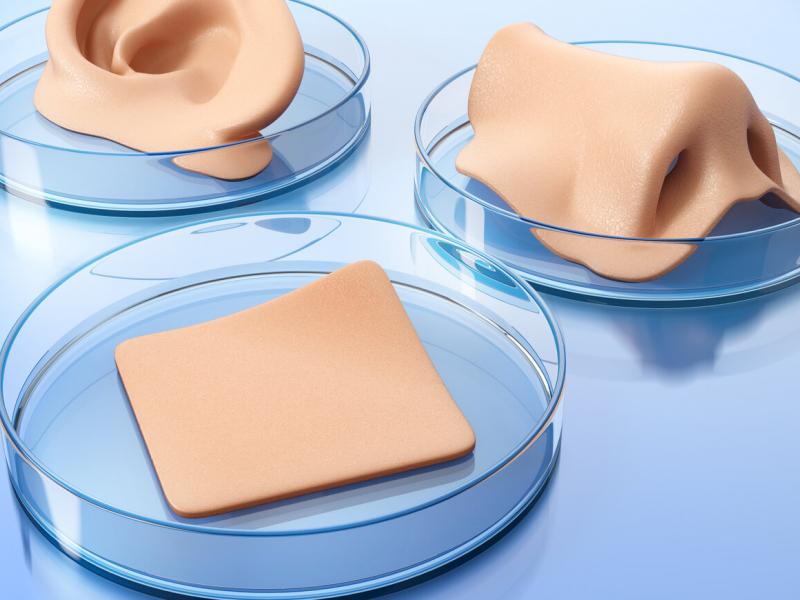

Clinical applications in Turkey
In Turkey, bioprinting offers multiple opportunities in regenerative medicine, particularly for:
- Skin reconstruction: Treatment of severe burns, chronic ulcers and skin defects.
- Tissue engineering: Creating grafts to repair damaged organs.
- Disease model development: Studying complex diseases and developing new therapies.
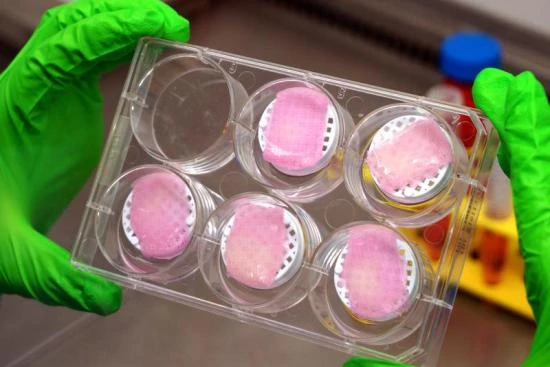
Skin bioprinting: Materials, processes, and challenges
Skin bioprinting requires rigorous materials and processes to faithfully reproduce the complex properties of native skin. Bioprinted skin substitutes must meet precise criteria for biocompatibility, mechanical properties, and cellular composition.
Biocompatibility and functionality
Bioinks and printed structures must be highly biocompatible to ensure optimal integration into host tissues. They must also promote metabolic exchange, i.e., allow the transfer of nutrients to cells and the removal of waste products. The surface chemistry of the materials used plays a critical role in cell adhesion and tissue proliferation.
Cell composition and tissue organization
Reconstructing the complex architecture of the skin requires precise control of cell deposition. The various cell types that make up the epidermis and dermis (keratinocytes, melanocytes, Merkel and Langerhans cells, fibroblasts, adipocytes) must be deposited with appropriate density and spatial distribution. Control of these parameters is essential to ensure the formation of a functional and durable tissue.
Mechanical and structural properties
The mechanical properties of bioprinted skin substitutes must be tuned to mimic those of native skin. Mechanical strength, porosity, and degradation rate are key parameters to optimize. Adequate porosity ensures efficient revascularization and promotes cell migration. Pore size, typically between 200 and 400 µm, must be sufficient to allow gas exchange and cell passage while providing protection against pathogens.
Biodegradation and tissue remodeling
Materials used for bioprinting must be biodegradable to allow for tissue remodeling and progressive replacement of the scaffold with newly formed tissue. The rate of degradation must match the kinetics of tissue regeneration. Ideally, skin substitutes should retain their structural integrity for several weeks to promote angiogenesis and cell repopulation.
3D skin bioprinting in Turkey
Our partner institutions in Turkey are at the forefront of 3D tissue bioprinting research. With significant investments and recognized expertise in regenerative medicine, they are actively contributing to the development of this innovative technology.
Their goal is to develop personalized therapeutic solutions for patients suffering from skin lesions by exploiting the full potential of bioprinting.
Share this page